4 Steps Developers Should Take To Use npm Securely
Table of Contents
Node Package Manager (npm) was a revolutionary addition to web application programming. It allowed developers to create small, reusable pieces of code and share them with the developer community.
npm gives developers massive flexibility and makes developing applications incredibly simple, but there are also potential pitfalls when it comes to npm security.
Here are four steps you should take right now to improve npm security for your business.
#1 Know which npm Packages You’re using
One of the significant parts of the culture of Node.js development is its embrace of the Linux philosophy that says that your programs should do one thing very well. Every application is kept small by starting from scratch, and adding only the pieces you need to accomplish the functionality that you’re aiming for.
Node applications have begun to grow in size and complexity along with its popularity. Node.js applications are increasingly expected to do more, and require more modules to complete their given tasks. You need MVC libraries like ExpressJS or Koa. Then you need testing frameworks, UI frameworks, and MongoDB clients. The list of dependencies continues to grow longer and longer.
The more dependencies you have within your application, the harder it is to ensure npm security. You should have a comprehensive inventory of all npm packages you use, the versions of each one, and the reason that you’re using them.
In order to stay on top of npm security, new packages shouldn’t be added on a whim. Introduce new packages only after you’ve verified that you can’t achieve the functionality with a module you’re already using.
#2 Update your npm packages
If it ain’t broken, don’t fix it, right? Most npm packages get updates all the time. Some updates are defined as minor releases and some as patch releases. Patch releases are very important, as some are fixing known vulnerabilities which were reported and information about the vulnerability and its exploitation is public information.
You need to make sure you know how to continuously update your npm packages.
#3 Use npm audit
The latest versions of npm feature the ability to scan your dependencies for security vulnerabilities. The npm audit command will scan direct dependencies, devDependencies, bundled dependencies, and optional Dependencies. npm will grab these and send them up to your default repository, asking for any known vulnerabilities.
npm will run npm audit every time you run npm install. It’s also recommended to run npm audit at crucial moments of your CI cycle to prevent vulnerable dependencies from creeping in.
Several options are available for npm audit that make gathering information about vulnerabilities and how to fix them easier. Here’s a list of useful npm audit parameters and what they do:
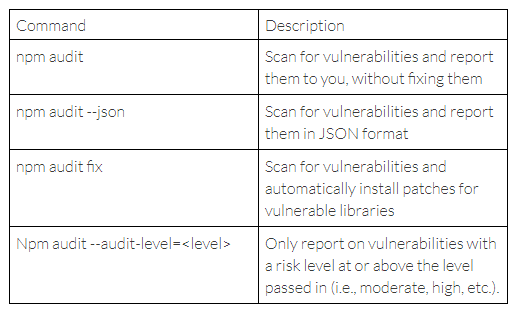
Check out the npm audit documentation for the details on what arguments are possible and how to use them.
#4 Use a private npm repository
For the highest level of npm security, set up a private npm repository inside your firewall instead of depending on a public repo. Public repositories are convenient, allowing developers to get up and running quickly. However, you’ll run the risk of your npm modules’ security becoming compromised.
There are two main ways this occurs. First, many GitHub accounts of maintainers have horrible passwords. Many were found to have passwords that matched their username or even “123456.” Such sloppy security practices make it trivial to take over a contributor’s account and add code that shouldn’t be there. Many of these passwords were for accounts with publishing access to the repository.
Another way attackers gain access is through social engineering. In November 2018, a hacker gained access to the event-stream package by offering to take over the project. The original owner didn’t have the time or desire to continue working on it. Under the guise of a good samaritan, the hacker stole private keys from users’ cryptocurrency accounts.
There are several tools available to help build your repo. After creating a repo, you can vet modules for security and usability before adding them. You can also create custom modules for developers and add them to the repo. Then, configure your developers’ machines to pull from the private repo by default.
Once you’ve set up a private repo, make sure you take all the steps necessary to keep it secure. That includes monitoring it continuously, and providing a smooth workflow for developers to request to add new packages. It’s also important to keep the modules in your private repo updated by regularly checking with npm audit or other tools.
npm security is possible
Visibility and control are essential skills to develop when managing npm security. If you don’t create a private repo, keep an eye on the packages that you use. Use tools like npm audit and open source scanning tools to help make the process automatic.
When your supply chain is secure, your apps will be too.