What You Need To Know About Application Security Testing Orchestration

Table of Contents

As the security threat landscape continues to evolve, choosing the best application security testing tools is just the first challenge for organizations investing in AppSec. Next, organizations need to figure out how to best orchestrate the application security testing technologies they are using in order to get the most out of them without losing valuable time. That’s where application security testing orchestration comes in.
Organizations today need to orchestrate their application security testing tools to ensure teams get full visibility and control over both proprietary and open source security vulnerabilities, throughout the development life cycle.
What Is Application Security Testing Orchestration?
The term application security testing orchestration is relatively new, and was introduced by Gartner’s Hype Cycle for Application Security, 2017. The report explains that “Application security testing orchestration (ASTO) integrates security tooling across a software development life cycle (SDLC), typically as part of DevSecOps initiatives.”
Engineering, Ops, and security teams today are doing their best to achieve a highly secure software development life cycle (SDLC) and an effective DevSecOps practice. The application security testing market offers a proliferation of solutions — each promising software development organizations the best tools to help them address the threats to their applications’ security.
Application security testing orchestration is crucial in helping teams manage these tools and the data they provide, in one centralized location. This helps organizations make sure all potential risks are tracked and addressed as soon as possible.
As Thomas Scanlon explains in Carnegie Mellon University’s Software Engineering Institute blog: “The idea of ASTO is to have central, coordinated management and reporting of all the different AST tools running in an ecosystem.”
Why We Need Application Security Testing Orchestration
The growing number, complexity, and variety of application types that organizations are using demands comprehensive testing solutions. Teams are moving from traditional web applications to modern applications that leverage client‑side software and microservices architecture. The fast-paced evolution of application development across diverse CI/CD environments and platforms requires innovative application testing tools, and the market is exploding with them.
There is a wide variety of application security testing tools in the market today, each offering different features, technologies, and approaches to protecting applications, from security scanning to runtime protection, spanning a wide range of development and production environments and tools.
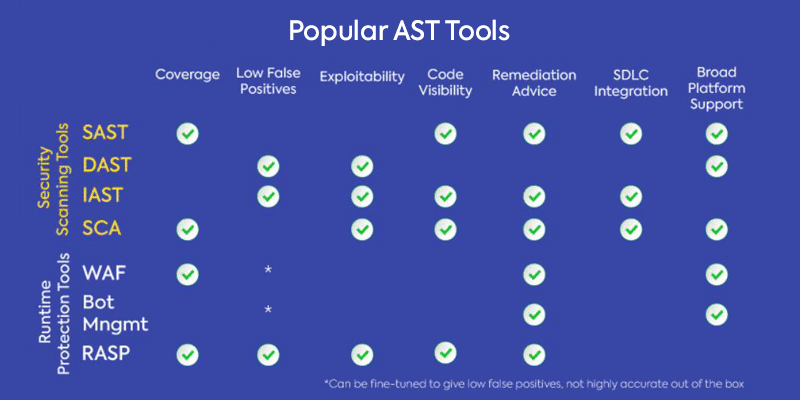
The most common security scanning tools in use today are:
-
SAST — Static application security testing, a white-box testing method where source code is analyzed from the inside out while components are at rest.
-
DAST — Dynamic application security testing, a type of black-box security testing that tests applications by attacking them from the outside.
-
IAST – Interactive application security testing, which works from within an application through instrumentation of the code to detect and report issues while the application is running.
-
SCA — Software composition analysis which scans the code base to provide visibility into open source and third party components.
The most common runtime protection tools include:
-
Web Application Firewall (WAF) that filters, monitors, and blocks HTTP traffic to and from web applications,
-
Bot Management, which distinguishes between good bots and bad bots instead of simply blocking all non-human traffic.
-
RASP — Runtime application self-protection, designed to detect and prevent attacks on applications in real-time from the inside.
These are just some of the application security testing tools in use today, and each one has its own pros and cons, and focuses on different stages in the DevSecOps pipeline. Most organizations will use as many as five different tools to cover all aspects of application security testing. While this helps to ensure relative coverage, manually managing all the tools and the data that they provide has become a major challenge. It often makes the process heavy, slow, and costly, not to mention the need for seasoned security experts with the knowledge and experience required to ensure security throughout the layered and complex systems we use.
The ever-evolving threat landscape and the laundry list of security alerts provided by multiple AST tools demands teams find an efficient way to prioritize and remediate security risks as soon as they are detected. Application security testing orchestration helps teams achieve their end goal, which is a quick remediation of the most urgent security threats.
The Benefits Of Application Security Testing Orchestration
The Gartner Hype Cycle for Application Security, 2017 report also describes the business benefits of application security testing orchestration solutions, and states that they “aid security, development and operations teams in coordinating the many security tests that should be performed on code. As such, these solutions can be a significant enabler in implementing DevSecOps initiatives, and they promise substantial benefits to the organization in terms of more consistent testing and smoother operations.”
Successful application security testing orchestration will run automatically in the background, combining the relevant data and alerts collected from an organization’s various AST tools to provide accurate and comprehensive information, insights, and even prioritization and remediation processes. As the Gartner report stated, this technology offers organizations a number of benefits.
One significant benefit is the consolidation of the data and reporting. Rather than having to spend valuable time sorting through reports and feeds from a collection of different tools, application security testing orchestration provides teams with a comprehensive and accurate snapshot of an organization’s application security posture. Reporting becomes easy and data more accessible, enabling teams to get an overview or drill down into specific information so that they can gain a full understanding of the threat landscape and their security posture.
{BANNER}
Knowledge is power, and the availability of comprehensive data and insights into their application security status helps organizations further improve their application security practices. Consolidating the data in one centralized location allows organizations to set and track KPIs, create a cross-organizational security policy and ensure that it is implemented across all teams, minimizing friction and encouraging transparency and communication.
Application security testing orchestration boosts security by bridging the gap from detection to remediation. As security testing tools are implemented early in the development process, orchestration can help streamline vulnerability management, automatically implementing policies that help development and security teams prioritize and remediate security vulnerabilities as early as possible.
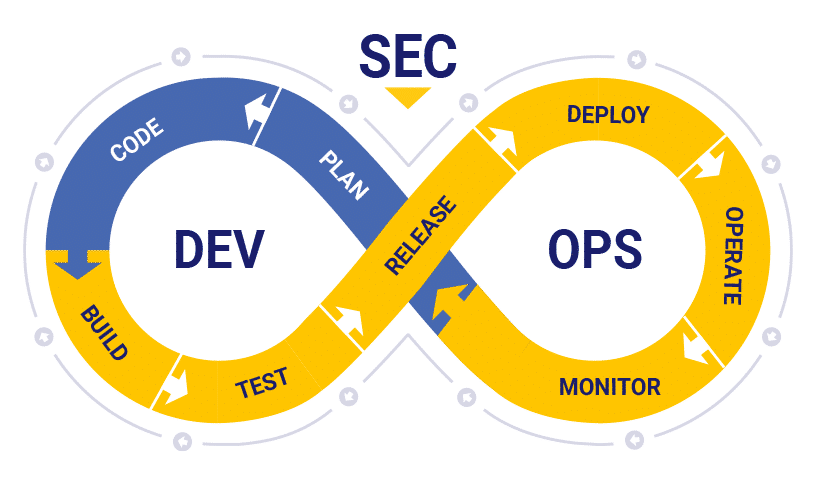
Application Security Testing Orchestration Is An Essential Step Towards DevSecOps Maturity
The DevSecOps approach demands organizations embrace automation, update their design and deployment processes to test early and often, and ensure that all teams share ownership of security. Application security testing orchestration addresses all of these requirements.
Implementing automated and continuous application security testing orchestration enables teams to easily manage a diverse selection of security testing tools and leverage them to address security threats in the most effective and efficient way possible.
As the application security testing space evolves, application security testing orchestration can help organizations achieve DevSecOps maturity by enabling them to implement a DevSecOps approach to application security across all teams. Orchestration will allow them to use automated tools and continually address security vulnerabilities’ prevention, detection, prioritization, and remediation, throughout the SDLC.