Table of contents
Best SAST tools: Top 10 solutions in 2025
What are SAST tools?
SAST (Static Application Security Testing) tools analyze an application’s source code to identify potential security vulnerabilities without executing the code. They are crucial for finding security flaws early in the development lifecycle, helping developers address issues before they become more costly and difficult to fix.
Unlike dynamic analysis techniques, SAST operates without executing the program, focusing entirely on the static codebase. This approach allows SAST tools to detect security flaws, such as injection vulnerabilities, insecure coding practices, and critical misconfigurations before an application is ever run in production or tested by end-users.
What modern SAST tools do:
- Prioritize real risk: They filter vulnerabilities by exploitability instead of flooding teams with raw findings.
- Fit developer workflow: They integrate scans into IDEs, pull requests, and CI/CD pipelines with minimal latency.
- Control noise: They baseline results, suppress duplicates, and reduce false positives through contextual analysis.
- Automated remediation workflows: They provide AI-driven fix suggestions and automated triage to accelerate patching.
- Keep up with technology: They expand coverage to new languages, frameworks, and AI-driven development practices.
- Scan source code: They examine the code (source, byte code, or binaries) to detect potential vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and buffer overflows.
- Provide feedback to developers: SAST tools integrate into development workflows, offering real-time feedback on security issues as developers write code.
- Automate vulnerability detection: They automate the scanning process, helping to identify vulnerabilities automatically.
- Integrate with development pipelines: They can be integrated into CI/CD pipelines, allowing for continuous security checks during the development process.
- Offer reporting and remediation guidance: SAST tools often provide detailed reports on vulnerabilities, including their location and potential impact, and may offer guidance on how to fix the issues.
Examples of SAST tools:
- Mend.io: Provides SAST integrated with dependency and supply chain security, helping manage open-source risks alongside code scanning.
- Semgrep: Lightweight, rule-based SAST tool with AI-assisted filtering to reduce false positives and integrate fixes into developer workflows.
- SonarQube: Broad static analysis platform that combines SAST with code quality checks and compliance reporting across multiple languages.
- Checkmarx: Enterprise SAST platform offering deep scanning, AI-powered query generation, and uncompiled code analysis.
- Veracode: Cloud-based SAST solution focused on whole-program analysis, low false positives, and developer-first integration.
- OpenText: Formerly Fortify, offering enterprise-grade SAST with AI-driven prioritization and flexible deployment options.
- Snyk Code: Developer-focused SAST tool providing real-time scans and context-aware autofixes inside IDEs and pull requests.
- Black Duck Software: Focuses on software supply chain security with SBOM management, compliance enforcement, and CI/CD integration.
- HCL Software: Enterprise vendor offering large-scale code scanning with AI-driven insights and broad enterprise deployment metrics.
- GitHub Advanced Security: Provides CodeQL-based SAST, dependency review, and secret scanning natively within GitHub repositories.
What modern SAST tools do
Modern SAST tools have evolved beyond simple static scans to address the realities of fast-paced software development. They aim to be accurate, usable, and adaptable to modern engineering practices:
- Prioritize real risk: Instead of overwhelming teams with raw findings, modern SAST tools demonstrate exploitability by tracing proof paths through the code. This helps developers see whether an issue is reachable and exploitable, filtering out false positives and highlighting risks that matter.
- Fit developer workflow: To be effective, security checks must fit into the developer’s workflow. Modern tools run lightweight scans inside IDEs and pull requests with low latency. This enables developers to catch vulnerabilities as they write or review code, without slowing down delivery.
- Control noise: Noise reduction is critical. Modern tools baseline results across scans, suppress duplicates, and surface only new or changed issues. AI is used to cluster similar findings and reduce false positives, making security feedback more actionable.
- Automated remediation workflows: Beyond detection, modern SAST provides remediation support. AI-driven suggestions, code fixes, and automated triage workflows reduce the time between identifying a vulnerability and deploying a fix. This helps security scale across large development teams.
- Keep up with technology: Finally, modern SAST keeps pace with emerging technologies. They support new languages, frameworks, and coding paradigms driven by AI coding assistants and modern microservices architectures, ensuring coverage stays relevant as development practices evolve.
Notable SAST tools
1. Mend.io
Mend SAST, an agentic static analysis tool, stops new vulnerabilities at the point of code creation. It delivers AI-powered fixes and immediate feedback directly into the AI development workflow, enabling developers to resolve security issues, whether human or AI-generated, the moment they appear.
Key features include:
- Agentic SAST support for AI code assistants that autonomously finds and fixes code flaws pre-commit.
- Reduced noise and high precision to pinpoint new vulnerabilities linked to recent changes, delivering 38% better precision and 48% better recall than competitors.
- Pre-production AI-powered fixes with every commit that are 46% more accurate than competitors, allowing developers to remediate risks without context switching.
- Near real-time feedback in the repo with scans up to 10x faster than traditional SAST tools, keeping pace with rapid AI development.
- Cloud compliance and governance with on-premises scanning to keep sensitive data private while enabling cloud-based reporting, quality gates, and workflow automations.
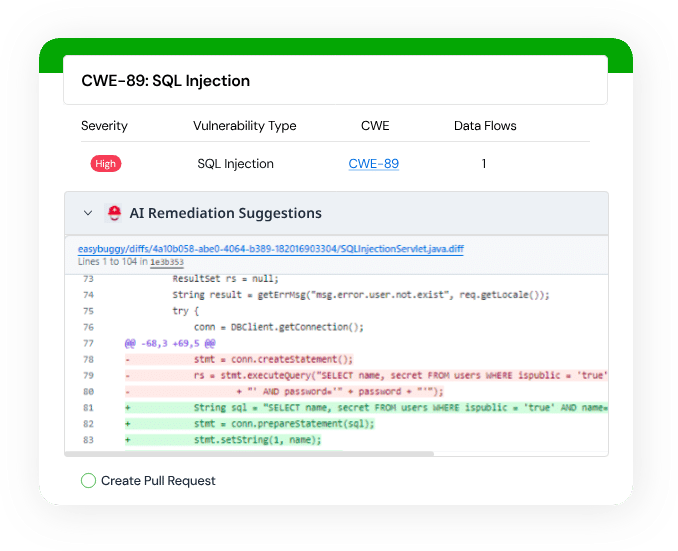
2. Semgrep

Semgrep is a static analysis tool to help developers detect and remediate security issues in code with minimal noise. It uses AI-assisted analysis and contextual filtering to reduce false positives, making its findings more actionable for developers.
Key features include:
- False positive reduction: Uses AI-powered filtering and dataflow reachability analysis to suppress irrelevant alerts and surface only actionable findings
- Integrated developer feedback: Delivers contextualized alerts and fixes directly within PR comments, IDEs, or Jira
- Automated remediation: Provides remediation advice and code fixes via Semgrep Assistant
- CI/CD integration: Runs in CI/CD pipelines with a median scan time of 10 seconds, supporting rapid development cycles
- Custom policy enforcement: Enables programmatic enforcement of security policies and OWASP Top Ten protections through guardrails and automation
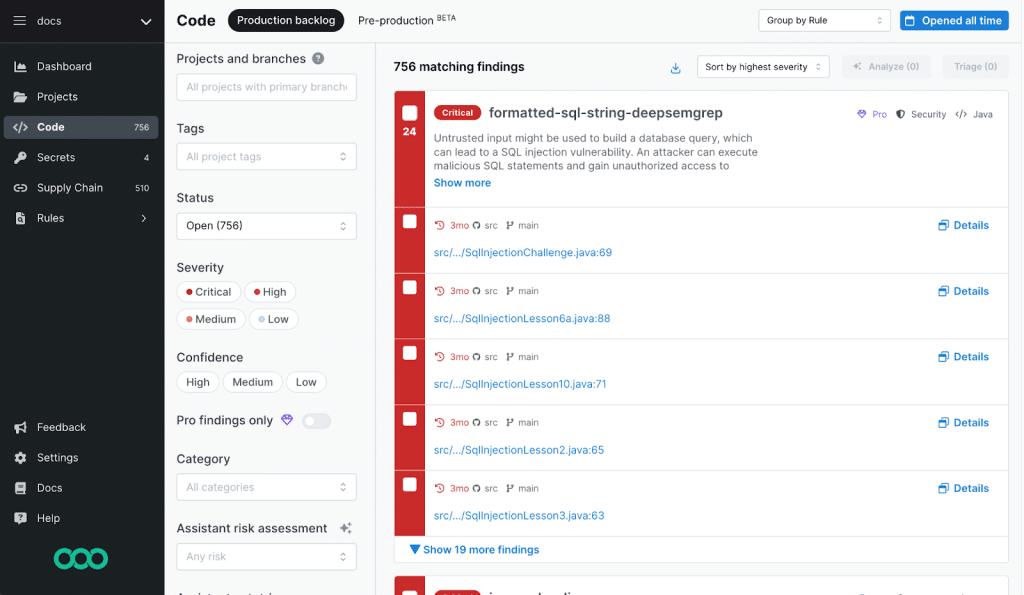
Source: Semgrep
3. SonarQube

SonarQube is a static analysis platform that helps organizations improve code security, quality, and compliance by scanning source code for vulnerabilities, bugs, and code smells. It includes SAST features that analyze application code and third-party open-source libraries.
Key features include:
- SAST engine: Extends dataflow analysis into third-party libraries to uncover deeply hidden vulnerabilities
- Dependency analysis: Scans open-source libraries and their transitive dependencies, reducing risks from external code
- Security rules aligned to standards: Maps issues to industry standards like OWASP Top 10, CWE Top 25, PCI DSS, and STIG
- Language support: Covers more than 30 languages including Java, C#, JavaScript, Python, C++, and PHP
- Taint analysis: Tracks untrusted user input across files and methods to detect critical security flaws
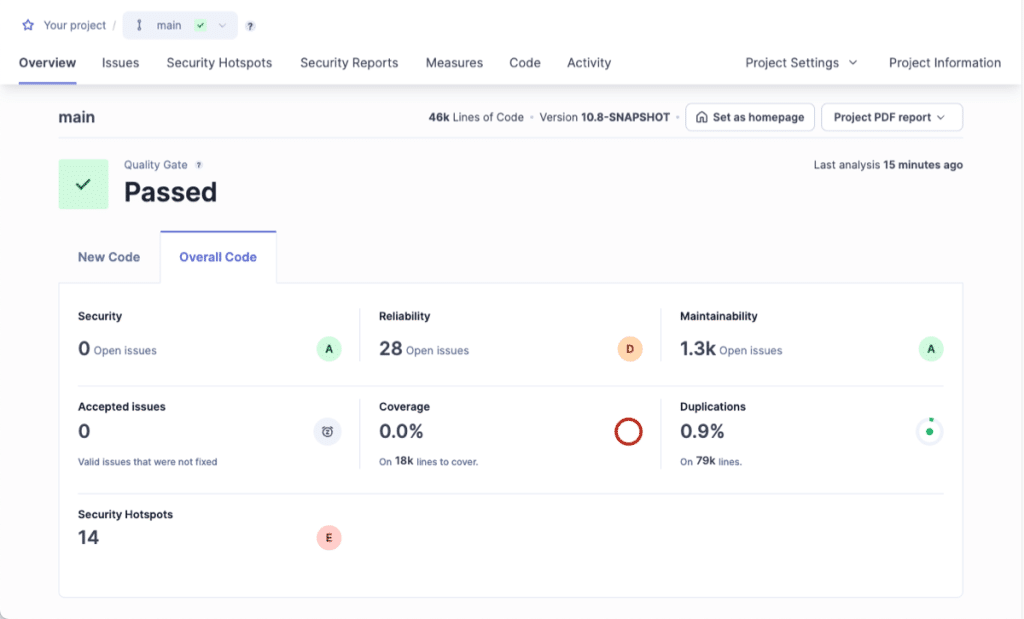
Source: SonarQube
4. Checkmarx

Checkmarx is a SAST platform to deliver security insights across the software development lifecycle. It offers fast code scanning with minimal developer disruption. It supports a range of languages and frameworks and integrates into development workflows, enabling teams to identify, prioritize, and remediate vulnerabilities in uncompiled code.
Key features include:
- Adaptive vulnerability scanning: Balances speed and depth by tailoring scans to surface the most relevant issues for each application
- Best fix location identification: Highlights the optimal place in the codebase to apply fixes, simplifying remediation
- AI query builder: Uses artificial intelligence to create customized security queries, improving accuracy and relevance
- AI security champion: Assists developers with AI-guided remediation and secure coding practices
- Uncompiled code scanning: Enables early detection of security issues before code is compiled, reducing risk during development
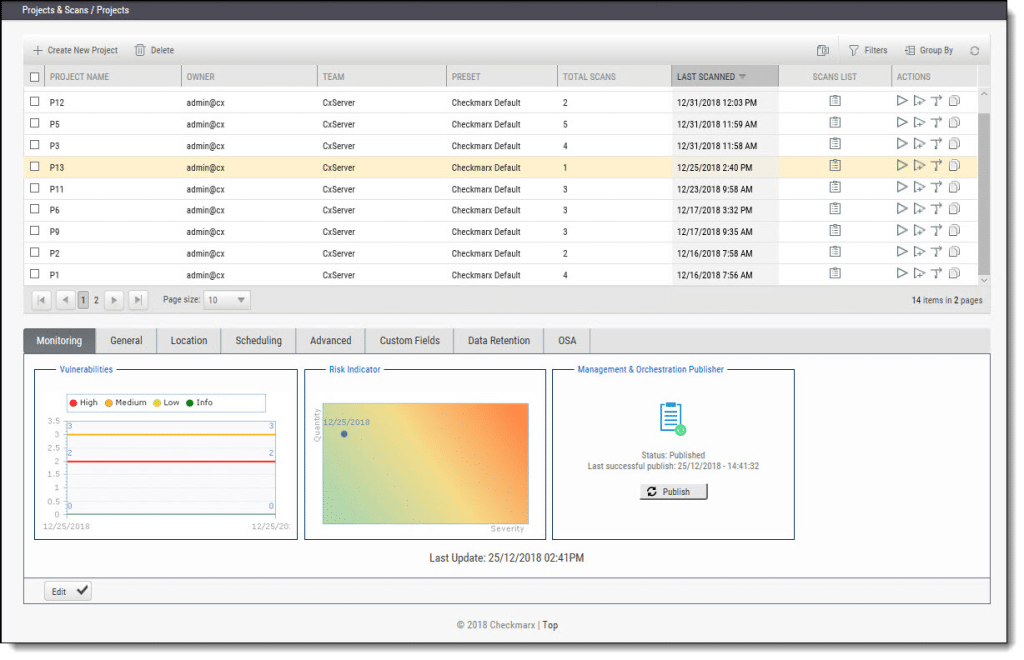
Source: Checkmarx
5. Veracode

Veracode is a SAST platform that delivers low-noise code scanning integrated across the software development lifecycle. It combines whole-program analysis with broad language and framework coverage to identify exploitable vulnerabilities early, without requiring extensive configuration.
Key features include:
- Whole-program analysis: Performs analysis to accurately detect flaws across the full application without complex tuning
- Language & framework coverage: Supports scanning of code written in over 100 languages and frameworks
- Developer-first integration: Embeds directly into IDEs, pipelines, and repositories for fast, in-context security feedback
- Low false positives: Delivers precise results out of the box, reducing noise and improving developer productivity
- IDE and pipeline scans: Enables scanning at multiple stages of development, from coding to deployment
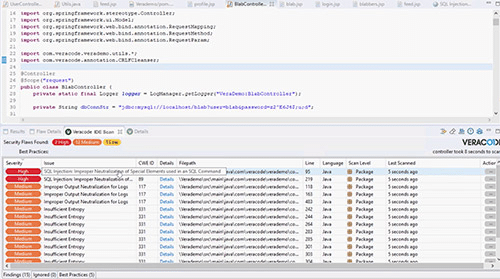
Source: Veracode
6. OpenText

OpenText static application security testing (formerly Fortify) is a SAST platform to detect vulnerabilities early in the software development lifecycle with low noise. It integrates into CI/CD pipelines and supports AI-driven prioritization and deep code analysis.
Key features include:
- AI-driven accuracy: Uses AI-assisted analysis to reduce false positives and prioritize critical vulnerabilities
- Language & framework support: Scans code in 33 languages and over 350 frameworks, including Java, and .NET, Python
- Integration ecosystem: Natively integrates with developer tools like GitHub, GitLab, Jenkins, Azure DevOps, Eclipse, and VS Code
- Customizable scan depth: Lets teams balance scan performance and detail with tunable analysis settings
- Cloud-native and flexible deployment: Offers SaaS, private cloud, and on-premises options to match enterprise infrastructure needs
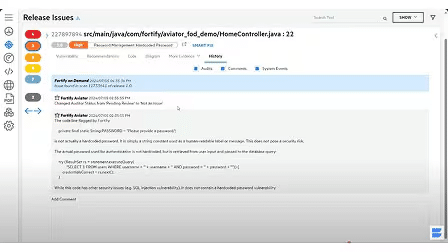
Source: OpenText
7. Snyk Code

Snyk Code is a developer-focused SAST product that provides real-time scanning and pre-validated, context-aware fixes in IDEs and pull requests.
Key features include:
- Real-time scanning and auto-fixing in IDEs and pull requests without builds, using pre-screened fixes via Snyk Agent Fix.
- Actionable results with context-specific explanations, enabling one-click application of pre-validated fixes directly where developers work.
- Broad language, IDE, and CI/CD coverage, including extensive support for LLM-related libraries such as OpenAI and Hugging Face.
- Self-hosted AI engine and large knowledge base modeling 25M+ data flows, continually improved through open source community learning.
- Risk-based prioritization that emphasizes newly deployed or publicly exposed issues, reducing noise and focusing attention on critical code paths.
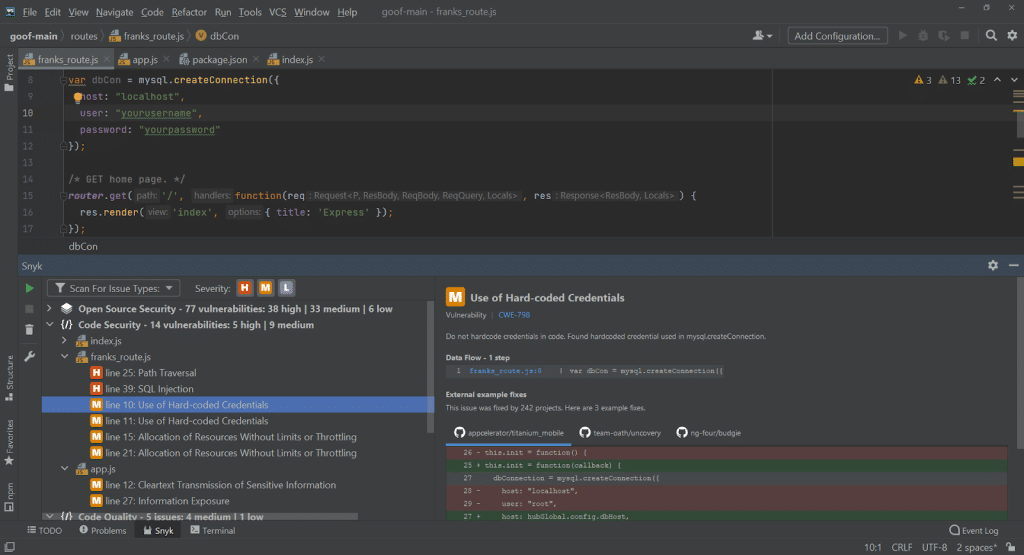
Source: Snyk
8. Black Duck Software

Black Duck Software is an application security platform focused on software supply chain assurance and risk management, with SBOM management and CI/CD integrations.
Key features include:
- Software supply chain security with SBOM management, addressing dependencies across the lifecycle to meet compliance and policy requirements.
- Orchestrates and correlates testing across tools and vendors, maintaining development speed while consolidating security signals for unified oversight.
- Integrations across the SDLC and CI/CD pipelines to automate testing at scale without imposing additional friction on delivery workflows.
- Enterprise-scale risk management with centralized visibility, policy-driven prioritization, and automated workflows aligned to organizational objectives.
- Support for safety-critical software programs emphasizing reliability and compliance, helping deliver secure, defect-free releases under strict requirements.
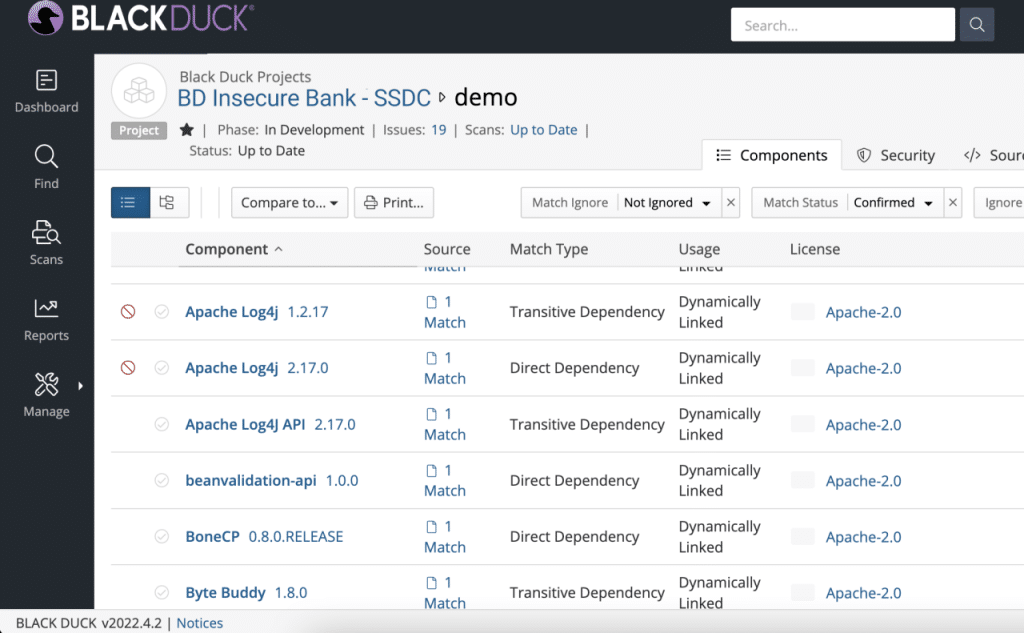
Source: BlackDuck
9. HCL Software

HCL Software provides enterprise software spanning cybersecurity, AI-powered intelligent operations, and business applications, with published metrics for code scanning throughput and customer reach.
Key features include:
- Cybersecurity solutions presented alongside AI-powered intelligent operations and business applications within the HCLSoftware product portfolio.
- Impact metrics cite 1.5 million lines of code scanned per hour across deployments, reflecting code analysis activity at significant operational scale.
- Customer footprint and operations metrics emphasize large reach and secured endpoints, indicating established deployment across enterprise environments.
- Resources and guidance available through the HCLSoftware Smart AI Assist portal, supporting discovery of products, practices, and security information.
- Recognition in analyst reports and peer review sites listed on the homepage, highlighting market presence across relevant software categories.
Source: HCL Software
10. GitHub Advanced Security

GitHub Advanced Security provides code and secret security features for GitHub repositories, including code scanning with CodeQL, dependency controls, and secret leak prevention.
Key features include:
- Code scanning using CodeQL or third-party tools, with optional CodeQL CLI for local analysis and upload to GitHub.
- Copilot Autofix generates automatic fixes for code scanning alerts to accelerate remediation directly within pull requests.
- Security campaigns and organization-wide security overview to manage risk reduction initiatives and track exposure across repositories.
- Dependency review and premium Dependabot features, including custom auto-triage rules to manage alerts at scale before merging.
- Secret scanning and push protection, including Copilot secret scanning, custom patterns, and delegated bypass for governed exceptions.
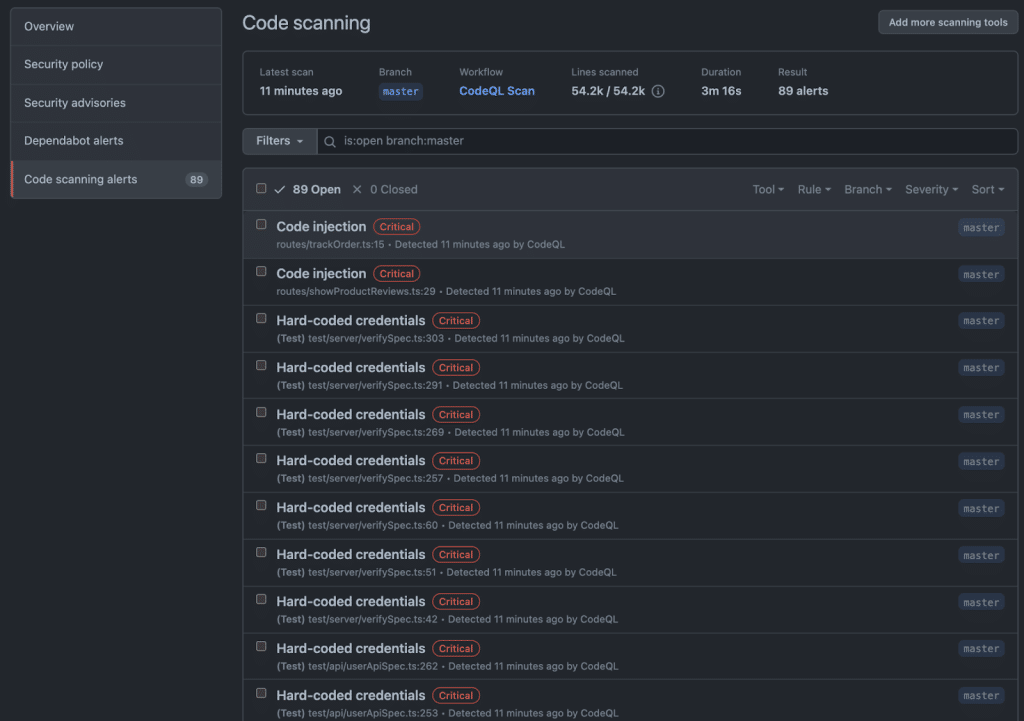
Source: GitHub
Best practices for using SAST tools
Here are some of the ways that organizations can improve their use of SAST tools.
1. Integrate where developers work
SAST tools are most effective when they meet developers where they write and review code. Embedding scans directly into IDEs and pull requests ensures that security checks happen in real time without interrupting workflows. This reduces the feedback loop, allowing developers to fix vulnerabilities before they move downstream, where remediation costs increase. Lightweight, incremental scans are preferable to heavy full-build analyses at this stage, as they provide fast and actionable results.
Integrating SAST into CI/CD pipelines is equally important to maintain DevOps speed. Security checks must run in parallel with build and deployment steps, not as blockers that slow delivery. A well-integrated SAST solution provides quick pass/fail signals, with detailed findings available for deeper inspection. This allows teams to maintain velocity while still enforcing consistent security guardrails at every stage of development.
2. Prioritize with context
SAST findings can easily overwhelm teams if presented without prioritization. Contextual triage using exploitability, impact, and code relevance helps teams focus on vulnerabilities that matter. Modern SAST tools can perform reachability analysis to determine if a flaw is actually exploitable within the application’s execution paths, reducing noise and false positives. This allows developers to concentrate effort on fixing issues that pose real security risks rather than chasing low-value alerts.
Stack awareness is another key factor in prioritization. A vulnerability that affects a critical service written in production languages should take precedence over an issue in a test harness or a deprecated component. AI-driven triage can automate this process by ranking vulnerabilities based on business-critical factors, ensuring that limited developer resources are spent on the flaws most likely to be exploited.
3. Accelerate remediation
Detection alone is insufficient if remediation lags. SAST tools should provide developers with AI-assisted fixes, code snippets, or precise guidance on where and how to patch issues. Automated remediation suggestions help reduce mean time to repair (MTTR) and ensure that fixes are aligned with the programming language and framework in use. This prevents wasted time on generic or inapplicable fixes that developers would otherwise need to adapt manually.
Autofix features can further accelerate remediation when combined with mandatory review steps. Developers receive proposed code changes that resolve vulnerabilities, which they can then validate and merge. This keeps control in the hands of engineers while eliminating repetitive manual patching. At scale, automated remediation workflows reduce backlog, improve consistency, and free up developer capacity for feature development.
4. Stay current with tech shifts
The programming landscape evolves quickly, and SAST tools must keep pace to remain relevant. Emerging languages like Rust, Dart, and Solidity introduce new security models and risks that older scanning rules may not detect. Similarly, AI frameworks such as LangChain, PyTorch, and TensorFlow bring unique attack surfaces, including prompt injection and model manipulation vulnerabilities. Organizations that fail to update SAST rules risk leaving critical blind spots in their coverage.
Staying current requires continuous updating of rule sets and vulnerability databases. Security teams should regularly review vendor updates, community rules, and new research on language-specific flaws. Some modern SAST platforms support dynamic rule delivery, ensuring tools are always aligned with the latest threats. By maintaining up-to-date coverage, organizations can proactively secure applications against both traditional vulnerabilities and new classes of risks driven by AI adoption and emerging technologies.
5. Measure outcomes, not just scans
Running frequent scans is not enough—organizations must track whether vulnerabilities are actually being resolved. Metrics such as fix rates, mean time to repair, and developer adoption rates provide a clearer picture of real security improvements. For example, a high scan frequency with a low fix rate indicates that findings are not actionable or not being prioritized effectively. Tracking these metrics ensures that SAST programs deliver measurable outcomes instead of generating unused reports.
Another key measure is scan latency in developer workflows. If pull request scans take too long, developers may bypass or resist the tool, reducing adoption. Continuous monitoring of latency and feedback loops helps maintain usability. By focusing on outcome-driven KPIs rather than raw scan counts, organizations can avoid shelfware scenarios where tools are present but not delivering value. This ensures security investments align with business goals and development velocity.
Conclusion
SAST tools play a critical role in secure software development by enabling early detection of vulnerabilities, integrating security into developer workflows, and providing actionable guidance for remediation. When combined with tailored rulesets, continuous monitoring, and developer education, they help organizations build software that is resilient against evolving security threats while maintaining development speed.